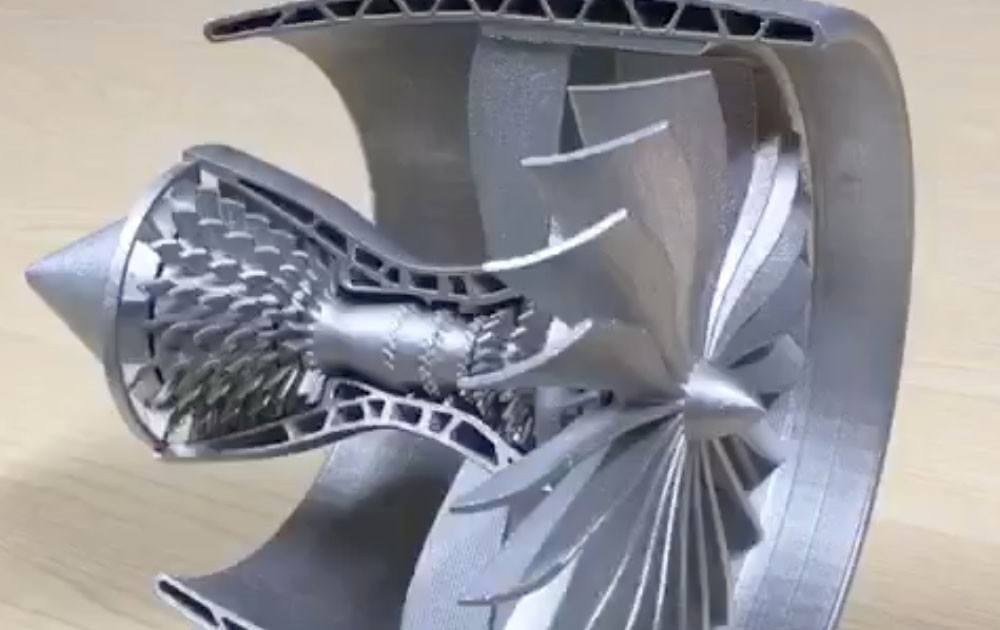
Metal 3D printing
Industry Introduction
Direct Metal Laser Forming (DMLS)
SLS manufactures metal parts. There are usually two methods, one is the indirect method, that is, the SLS of the polymer coated metal powder; the other is the direct method, that is, direct metal powder laser sintering (Direct Metal LaserSintering, DMLS). Since the direct laser sintering of metal powders in 1991 at the University of Chatofci in Leuvne, the direct sintering of metal powders into three-dimensional parts using the SLS process has been one of the ultimate goals of rapid prototyping. The main advantage of the DMLS process over indirect SLS technology is the elimination of expensive and time consuming pre- and post-processing steps.
Characteristics of direct metal powder laser sintering (DMLS)
As a branch of SLS technology, DMLS technology has basically the same principle. However, DMLS technology has a great difficulty in accurately forming metal parts with complex shapes. In the final analysis, it is mainly due to the "spheroidizing" effect and sintering deformation of metal powder in DMLS. The spheroidization phenomenon is to make the surface and periphery of molten metal liquid. The system composed of the surface of the medium has a minimum free energy, and the phenomenon that the surface shape of the molten metal changes to the spherical surface under the action of the interfacial tension between the liquid metal and the surrounding medium. Spheroidization will melt the metal powder and will not solidify to form a continuous and smooth molten pool. Therefore, the formed parts are loose and porous, resulting in failure of molding. Since the viscosity of the single-component metal powder in the liquid phase sintering stage is relatively high, "spheroidization" The effect is particularly serious, and the spherical diameter is often larger than the diameter of the powder particles, which causes a large number of pores to exist in the sintered part. Therefore, the DMLS of the single-component metal powder has obvious process defects and often requires subsequent processing, which is not in the true sense. Direct sintering".
In order to overcome the "spheroidization" phenomenon in the single-component metal powder DMLS, and the resulting process defects such as sintering deformation and density looseness, it is generally possible to achieve by using multi-component metal powders having different melting points or using pre-alloyed powders. . The multi-component metal powder system is generally composed of a high melting point metal, a low melting point metal and certain additive elements, wherein the high melting point metal powder acts as a framework metal and retains its solid phase core in the DMLS; the low melting point metal powder acts as a binder The metal is melted in the DMLS to form a liquid phase, and the resulting liquid phase coats, wets, and bonds the solid phase metal particles, thereby achieving sintering densification.